The recordings of this database are of rest tremor velocity in the index finger of 16 subjects with Parkinson's disease (PD) who receive chronic high frequency electrical deep brain stimulation (DBS) either uni- or bi-laterally within one of three targets:
- Vim = the ventro-intermediate nucleus of the thalamus (n=3),
- GPi = the internal Globus pallidus (n=7), or
- STN = the subthalamic nucleus (n=6).
This surgical procedure involves implanting an electrode into subcortical structures (Vim, GPi or STN) for long-term stimulation at frequencies greater than 100 Hz. The mechanism by which high frequency DBS suppresses tremor and reduces other symptoms in PD is unknown.
Parkinson’s disease is characterized by the progressive loss of dopamine neurons in the substantia nigra of the midbrain, and is associated with motor symptoms including tremor (usually rest tremor, though sometimes postural tremor), bradykinesia and rigidity. In Parkinson’s disease, tremor becomes more regular or harmonic, its frequency is shifted to a lower range (typically 4–6 Hz), its amplitude increases, the shape of its oscillations changes, and it fluctuates over time. These changes are subtle and intermittent at first, becoming more permanent and obvious as the disease progresses.

Figure 1. Two seconds of Parkinsonian rest tremor velocity (metres/second) recordings from subject g2 (stimulator implanted in the GPi) under four conditions: (a) no stimulation and no medication, (b) deep brain stimulation and no medication, (c) no stimulation and 150% medication, (d) deep brain stimulation and 150% medication. Note the zoomed vertical scale in (b), (c) and (d).
Chronic high frequency deep brain stimulation of the Vim can decrease tremor amplitude in a spectacular way. Deep brain stimulation of the GPi and STN have been shown to relieve not only tremor but also other symptoms of PD such as rigidity and dyskinesia. See Figure 1 for an example of the effect of deep brain stimulation of the GPi on tremor.
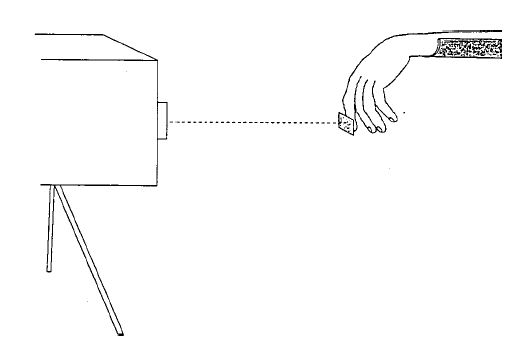
Figure 2. Velocity laser recording of rest tremor.
The raw data were obtained using a low intensity velocity-transducing laser that was directed at a piece of reflective paper on the subject’s index finger tip (Figure 2), with the output voltage proportional to the velocity of the finger.
DBS/Medication Conditions:
Tremor was recorded for approximately 60 seconds under various conditions:
- two conditions of DBS (on-off) and two conditions of medication
(L-dopa on-off)
[total: 55 recordings of approx 60 seconds each] - every 15 minutes when DBS was stopped for 60 minutes (medication off)
[total: 46 recordings of approx 60 seconds each]
Please note that not all subjects were tested under all conditions.
For the "medication off" condition, the subject did not take any medication for at least 12 hours. For the "medication on" condition, the subject took 150% of his or her morning dose of dispersible Modopar and testing began after the neurologist determined the medication had taken effect (approximately 40 minutes).
Subjects:
The 16 subjects can be divided into two groups:
- Subjects 1–8 with high amplitude tremor (HAT) who are receiving DBS to relieve tremor (Group 1), and
- Subjects 9–16 with low amplitude tremor (LAT) who are receiving DBS to relieve other symptoms such as rigidity or dyskinesias (Group 2).
The file subject_description.txt contains information on the 16 subjects:
| Information | Description |
|---|---|
| SUBJECT | 2 character subject identification: Stimulation target (v=Vim, s=STN, g=GPi), and Subject number (1-16) |
| AGE | Age at the time of testing (years) |
| GENDER | Male (n=11) or female (n=5) |
| STIM TARGET | Vim = ventro-intermediate nucleus
of the thalamus GPi = internal Globus Pallidus STN=subthalamic nucleus |
| BI/UNI-LATERAL | Bilateral stimulation (n=12) or unilateral stimulation (n=4) |
| EFF FREQ | Frequency (Hz) of effective stimulation (> 100 Hz) |
| INEFF FREQ | Frequency (Hz) of so-called ineffective stimulation (< 100 Hz) |
| INTENSITY | Stimulation intensity (V) |
| PULSE WIDTH | Stimulation pulse width (µsec) |
| MODE | Cont = continuous
stimulation, Cycl=cyclic stimulation (e.g. 1 minute on, 1 second off) |
| STIM CONTACTS | Listed in order of proximal
distal direction on quadripolar stimulating electrode: - negative polarity + positive polarity . not stimulated |
| YEAR DIAGNOSED | Year diagnosed with Parkinson's disease |
| YEAR DBS RIGHT | Year of right brain DBS surgery |
| YEAR DBS LEFT | Year of left brain DBS surgery |
| TOT DAILY MED | Total medication of morning, noon and evening doses (mg) |
| 150% SINGLE DOSE | Dose taken before testing "medication on" condition (mg) |
Filename Structure:
The file name structure of the records is:
- 2 character subject identification: stimulation target (v=Vim, s=STN, g=GPi) and subject number (1–16)
- 1 character tremor type: r = resting tremor
- 1 character DBS condition: e = effective (> 100 Hz), o = no stimulation
- (optional) 2 character time since stimulator arrest: if a 2 digit number follows the DBS condition, it indicates the number of minutes since the stimulation was stopped
- 1 character medication condition: n= medication on, f=medication off
- 3 character extension indicates the side tested: let = left index finger tremor, rit = right index finger tremor
Filename Examples:
- s6ren.let contains a recording (approx. 60 sec) of rest tremor in the left index finger of subject 6 in the "dbs on and medication on" condition: the subject had taken 150 % of his or her morning dose of L-dopa and was receiving "effective" stimulation of the STN.
- v4rof.rit contains a recording (approx. 60 sec) of rest tremor in the right index finger of subject 4 in the "dbs off and medication off" condition: the subject was off medication for at least 12 hours and the subject's stimulator (implanted in the Vim) was switched off.
- g1r30of.rit contains a recording (approx. 60 sec) of rest tremor in the right index finger of subject 1 at 30-minutes after the stimulator (implanted in the GPi) was switched off. Also, this subject was off medication for at least 12 hours.
Tremor Recordings:
The rest tremor recordings can be classified as one of 8 categories, for subjects with high amplitude tremor (HAT) and for subjects with low amplitude tremor (LAT):
- ren: Deep brain stimulation on, Medication on
HAT subjects: n=5 recordings
LAT subjects: n=8 recordings - ref: Deep brain stimulation on, Medication off
HAT subjects: n=5 recordings
LAT subjects: n=8 recordings - ron: Deep brain stimulation off, Medication on
HAT subjects: n=7 recordings
LAT subjects: n=8 recordings - rof: Deep brain stimulation off, Medication off
HAT subjects: n=6 recordings
LAT subjects: n=8 recordings - r15of: Deep brain stimulation off for 15 minutes,
Medication off
HAT subjects: n=3 recordings
LAT subjects: n=8 recordings - r30of: Deep brain stimulation off for 30 minutes,
Medication off
HAT subjects: n=4 recordings
LAT subjects: n=8 recordings - r45of: Deep brain stimulation off for 45 minutes,
Medication off
HAT subjects: n=3 recordings
LAT subjects: n=8 recordings - r60of: Deep brain stimulation off for 60 minutes,
Medication off
HAT subjects: n=4 recordings
LAT subjects: n=8 recordings
| Total: | HAT subjects: n=37 recordings LAT subjects: n=64 recordings |
The file file_description.txt contains a summary of recordings per subject in each category.
Reference:
Beuter, A., Titcombe, M.S., Richer, F., Gross, C., Guehl, D., 2001. Effect of deep brain stimulation on amplitude and frequency characteristics of rest tremor in Parkinson's disease. Thalamus & Related Systems, Volume 1 (3): 203–211 (published by Elsevier Science).
Name Last modified Size Description
Parent Directory -
r15ofh/ 18-Oct-2001 19:03 -
r15ofl/ 19-Oct-2001 20:37 -
r30ofh/ 18-Oct-2001 20:44 -
r30ofl/ 19-Oct-2001 20:41 -
r45ofh/ 18-Oct-2001 20:46 -
r45ofl/ 19-Oct-2001 20:55 -
r60ofh/ 18-Oct-2001 20:57 -
r60ofl/ 09-Nov-2001 20:52 -
refh/ 18-Oct-2001 17:41 -
refl/ 19-Oct-2001 20:26 -
renh/ 19-Oct-2001 16:34 -
renl/ 19-Oct-2001 20:19 -
rofh/ 18-Oct-2001 18:57 -
rofl/ 19-Oct-2001 20:35 -
ronh/ 09-Nov-2001 20:53 -
ronl/ 19-Oct-2001 20:32 -
DOI 19-Feb-2019 19:48 19
MD5SUMS 13-Jul-2005 08:26 328
SHA1SUMS 13-Jul-2005 08:26 434
SHA256SUMS 18-Sep-2007 18:40 701
RECORDS 27-Aug-2001 23:17 1.1K list of record names
local.css 28-Oct-2015 22:58 3.1K
subject_description.txt 01-Oct-2001 16:29 3.2K
vlaser.gif 19-Oct-2001 17:31 4.6K
g2.gif 19-Oct-2001 18:52 6.5K
file_description.txt 19-Oct-2001 00:44 11K
|
If you would like help understanding, using, or downloading content, please see our Frequently Asked Questions. If you have any comments, feedback, or particular questions regarding this page, please send them to the webmaster. Comments and issues can also be raised on PhysioNet's GitHub page. Updated Friday, 28-Oct-2016 22:58:42 CEST |
PhysioNet is supported by the National Institute of General Medical Sciences (NIGMS) and the National Institute of Biomedical Imaging and Bioengineering (NIBIB) under NIH grant number 2R01GM104987-09.
|