The arterial baroreflex arc is implemented according to the feedback
system illustrated in Figure 4. This system is aimed at
tracking a setpoint (![]() ) pressure through the following sequence of
events. The baroreceptors sense
) pressure through the following sequence of
events. The baroreceptors sense ![]() and relay this pressure to
the autonomic nervous system (ANS). The ANS compares the deviation
between the sensed pressure and
and relay this pressure to
the autonomic nervous system (ANS). The ANS compares the deviation
between the sensed pressure and ![]() with zero and then responds
by adjusting four parameters of the pulsatile heart and circulation in
order to keep the ensuing
with zero and then responds
by adjusting four parameters of the pulsatile heart and circulation in
order to keep the ensuing ![]() near
near ![]() . The four
adjustable parameters are
. The four
adjustable parameters are ![]() ,
,
![]() at end-systole
(
at end-systole
(
![]() ),
), ![]() , and
, and ![]() . The ANS controls these
parameters based on the history of
. The ANS controls these
parameters based on the history of
![]() specifically
according to the following nonlinear, dynamical mapping:
specifically
according to the following nonlinear, dynamical mapping:
The cardiopulmonary baroreflex arc is also implemented according to a
feedback diagram analogous to Figure 4. However, the
sensed pressure here is defined to be the effective right atrial
transmural pressure
(
![]() ) of
the pulsatile heart and circulation model.
) of
the pulsatile heart and circulation model.
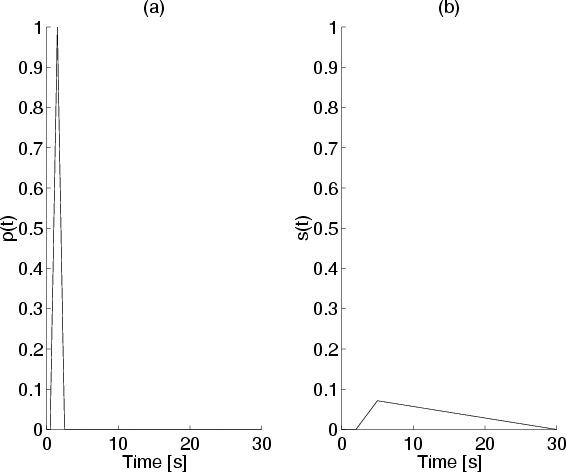 |
The direct neural coupling mechanism between respiration and heart
rate is characterized by a linear, time-invariant impulse response
which maps fluctuations in instantaneous lung volume (![]() ; see
Section 2.3) to fluctuations in
; see
Section 2.3) to fluctuations in ![]() . The impulse
response is defined here by a linear combination of
. The impulse
response is defined here by a linear combination of ![]() and
and ![]() ,
each of which are advanced in time by 1.5 s in order to account for
the noncausality of this mechanism [6,9].
,
each of which are advanced in time by 1.5 s in order to account for
the noncausality of this mechanism [6,9].